This blog posts contains links that I found with useful information.
What are IaaS, PaaS, SaaS, and CaaS?
Cloud computing has three main cloud service models: IaaS (infrastructure as a service), PaaS (platform as a service), and SaaS (software as a service). You might also hear IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS called cloud service offerings or cloud computing categories, but all of these terms refer to how you use the cloud in your organization and the degree of management you’re responsible for in your cloud environments.
In addition to these three broad categories, you may also come across other types of cloud services that incorporate other technologies, such as containers. For example, the rising adoption of containers and microservices architectures has led to the emergence of CaaS (containers as a service).
"As a service" typically means that the service model is offered by a third party in the cloud. In other words, you don’t have to purchase, manage, or use any hardware, software, tools, or applications from an on-premises data center. Instead, you can simply pay a subscription or pay based on consumption (pay-as-you-go) to access what you need on demand via an internet connection.
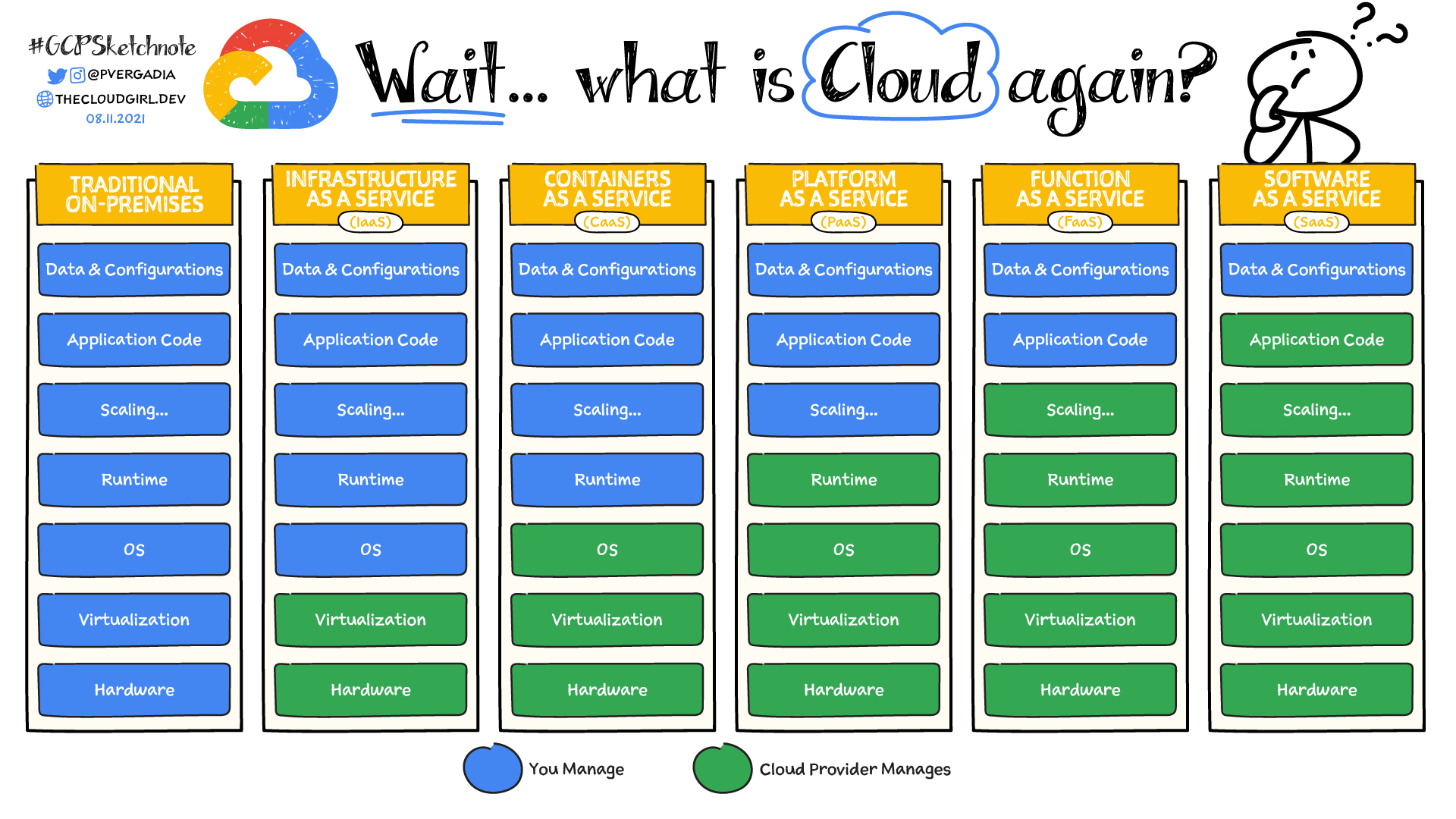
IaaS Infrastructure as a service, or IaaS, delivers on-demand infrastructure resources to organizations via the cloud, such as compute, storage, networking, and virtualization. Customers don’t have to manage, maintain, or update their own data center infrastructure, but are responsible for the operating system, middleware, virtual machines, and any apps or data.
CaaS Containers as a service, or CaaS, delivers and manages all the hardware and software resources to develop and deploy applications using containers. Sometimes viewed as a subset or an extension of IaaS, CaaS uses containers rather than VMs as its main resource. Developers and IT operations teams can use CaaS to develop, run, and manage applications without having to build and maintain the infrastructure or platform to run and manage containers. Customers still have to write the code and manage their data and applications, but the environment to build and deploy containerized apps is managed and maintained by the cloud service provider.
PaaS Platform as a service, or PaaS, delivers and manages all the hardware and software resources to develop applications through the cloud. Developers and IT operations teams can use PaaS to develop, run, and manage applications without having to build and maintain the infrastructure or platform on their own. Customers still have to write the code and manage their data and applications, but the environment to build and deploy apps is managed and maintained by the cloud service provider.
SaaS Software as a service, or SaaS, provides the entire application stack, delivering an entire cloud-based application that customers can access and use. SaaS products are completely managed by the service provider and come ready to use, including all updates, bug fixes, and overall maintenance. Most SaaS applications are accessed directly through a web browser, which means customers don’t have to download or install anything on their devices.
Additionally, you can find the term BaaS, which is Backend as a Service.
Some services and useful links
IaaS
- Digital Ocean - DigitalOcean Droplets which are Virtual Machines (apparently cheaper than larger cloud providers) offering monitoring, cloud firewalls, backups, snapshots, volume block storage, spaces object storage, load balancers, reserved IPs etc
PaaS
- Digital Ocean - DigitalOcean App Platform which is a fully managed platform that automatically handles infrastructure management, scaling, and deployments using Containers. You just need your Dockerfile and you can connect your Github repository so each commit will deploy a build. Some use cases can be Static Sites, Web Services, Workers, Jobs, Functions and Databases. This is a good video on how to deploy a Next.js app to Digital Ocean App Platform.
Serverless
These are different serverless backends you can use:
- Upstash - serverless data platform providing low latency and high scalability for real-time applications. They don't offer a self-hosted option. They have a generous free tier and serverless offering.
- Heroku - alternative to Vercel. Heroku is a cloud PaaS that supports lots of programming languages. Acquired by Salesforce in 2010.
BaaS
- Firebase - backend as a service (BaaS), offering authentication, blob storage, database, functions and more.
SaaS
Offline first apps
One of the first experiences I had with offline first development was with Realm and MongoDB Sync, a service that would provide bidirectional sync between the database running in your mobile phone (Realm) and the one in the cloud (MongoDB). This was discontinued in 2024. You can find the links to the repos in Github:
- Realm Swift - For a version of realm-swift without sync features, install version 20 or see the community branch
- Realm Kotlin
Alternatively, you can use the following services to cover this requirement:
- PowerSync - This is an alternative to App Services Sync from MongoDB that can use MongoDB as a database in the backend and SQLite in the phone or you can use PostgreSQL. Here you have a link explaining more.
- Ditto - Ditto is a real-time edge sync platform for mobile, web, IoT, and server apps. You can read more about the Ditto Reference Architecture and the Migration Guide from MongoDB App Services to Ditto
- AWS AppSync - AWS AppSync creates serverless Pub/Sub APIs to simplify development through a single endpoint to securely query, update, or publish data. Migration guide contains a guide on how to migrate to AWS AppSync.
Analytics
Aptabase - Aptabase is an Open Source alternative to Google Firebase Analytics for Next.js Apps. Find an example on how to integrate with your NextJS app in this GitHub repo
Self Hosted
Coolify - Coolify is an alternative to Vercel / Heroku / Netlify.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Recommendation Systems (GitHub repo)
This repository contains examples and best practices for building recommendation systems focusing on 5 key topics:
- Prepare and load the data
- Build models using deep learning recommendation algorithms
- Evaluate models using various performance measures
- Tune and optimise models
- Operationalise models in a production environment
Techniques to generate embeddings is a link to Google ML course explaining how embeddings work.
Why Large Language Models Struggle with Mathematical Reasoning?: very extensive article from Adnan Masood, PhD. explaining the limitations of LLMs for mathematical calculations.
Paper - GSM-SYMBOLIC: UNDERSTANDING THE LIMITATIONS OF MATHEMATICAL REASONING IN LARGE LANGUAGE MODELS : Paper from Apple explaining the limitations of the LLMs in mathematical reasoning.
Self hosting
- Cloudflare Tunnel - Create a tunnel to connect HTTP web servers, SSH servers, remote desktops, and other protocols safely to Cloudflare. Your server on-premises will be secured by Cloudflare.
- Marius Hosting - Self-hosted blog about hosting your apps in a Synology NAS using DiskStation and Container Manager.
CMS
- Cockpit CMS - Cockpit is a CMS that uses PHP and MongoDB as data base (also SQLite and more), is open source and can be self-hosted. Github repo
- Payload CMS - Open source CMS that can be deployed in Vercel or be self-hosted. It can use MongoDB or other databases.
Other CMSs are: Wordpress, Contentful, Sanity, Strapi
Alternatively, you can develop your own CMS using Next.JS and Vercel as it will simplify operations such as routes, DNS management, blob storage, image optimisation, CDN, WAF,…
MongoDB Links
Tool to quickly create MongoDB clusters using Docker -> Super useful tool created by a colleague from MongoDB (thanks Yuvi!) to create clusters with different topology either using brew or pip.
Databases
- Andy Pavlo Blog - Associate Professor with Indefinite Tenure of Databaseology in the Computer Science Department at Carnegie Mellon University. In particular is interesting their yearly reviews about databases.
- Luca Palmieri's blog In-depth overview of the pros and cons of several caching strategies to help you make an informed decision within the constraints of your own system.
- H2 database - In memory database usually used in development environments. Small footprint and written entirely in Java.
- Database of databases - A list of the existing databases, its history and level of support and maintenance
- The Race to replace Redis - Article written by Joe Brockmeier (Percona, Intel, Red Hat, Citrix and SUSE) in LWN.net on March 2024 about the controversial announcement that the Redis "in-memory data store" project would now be released under non-free, source-available licenses. Also talks about the different types of open source licenses (BSL, SSPL, BSD...)
- Milvus database: this is a high-performance vector database built for scale. It's the database used in the great service Credal to power their RAG solution. You can find more information on this article
Voices in the industry
- The Pragmatic Engineer: Gergely Orosz, Engineering Manager at Uber. Big tech and startups, from the inside. Relevant for software engineers and managers, interesting for those working at tech. Must have subscription to his podcast.
- [https://larahogan.me](Lara Hogan) Etsy's Engineering Director : She talks about the Manager Voltron.